
When you use “ls -l” you will get the details of directories content. Display Directory Information Using ls -ld Ls -lh (h stands for human readable form) : To display file size in easy to read format. Display File Size in Human Readable Format Using ls -lh Field 7 – File name: The last field is the name of the file.In this example, ‘Feb 16 00:19’ specifies the last modification time of the file. Field 6 – Last modified date and time: Sixth field specifies the date and time of the last modification of the file.In this example, ‘1176’ indicates the file size in bytes.

Field 5 – Size: Fifth field specifies the size of file in bytes.In this example, this file belongs to ”maverick’ group. Field 4 – Group: Fourth field specifies the group of the file.In this example, this file is owned by username ‘maverick’. Field 3 – Owner: Third field specifies owner of the file.In this example, 1 indicates only one link to this file. Field 2 – Number of links: Second field specifies the number of links for that file.If all three permissions are given to user(root), group and others, the format looks like -rwxrwxrwx Taking above example, -rw-rw-r– indicates read-write permission for user(root), read permission for group, and no permission for others respectively. The every 3 characters specifies read, write, execute permissions for user(root), group and others respectively in order. Field 1 – File Permissions: Next 9 character specifies the files permission.Following are the possible file type options in the 1st character of the ls -l output. In the example above the hyphen (-) in the 1st character indicates that this is a normal file.
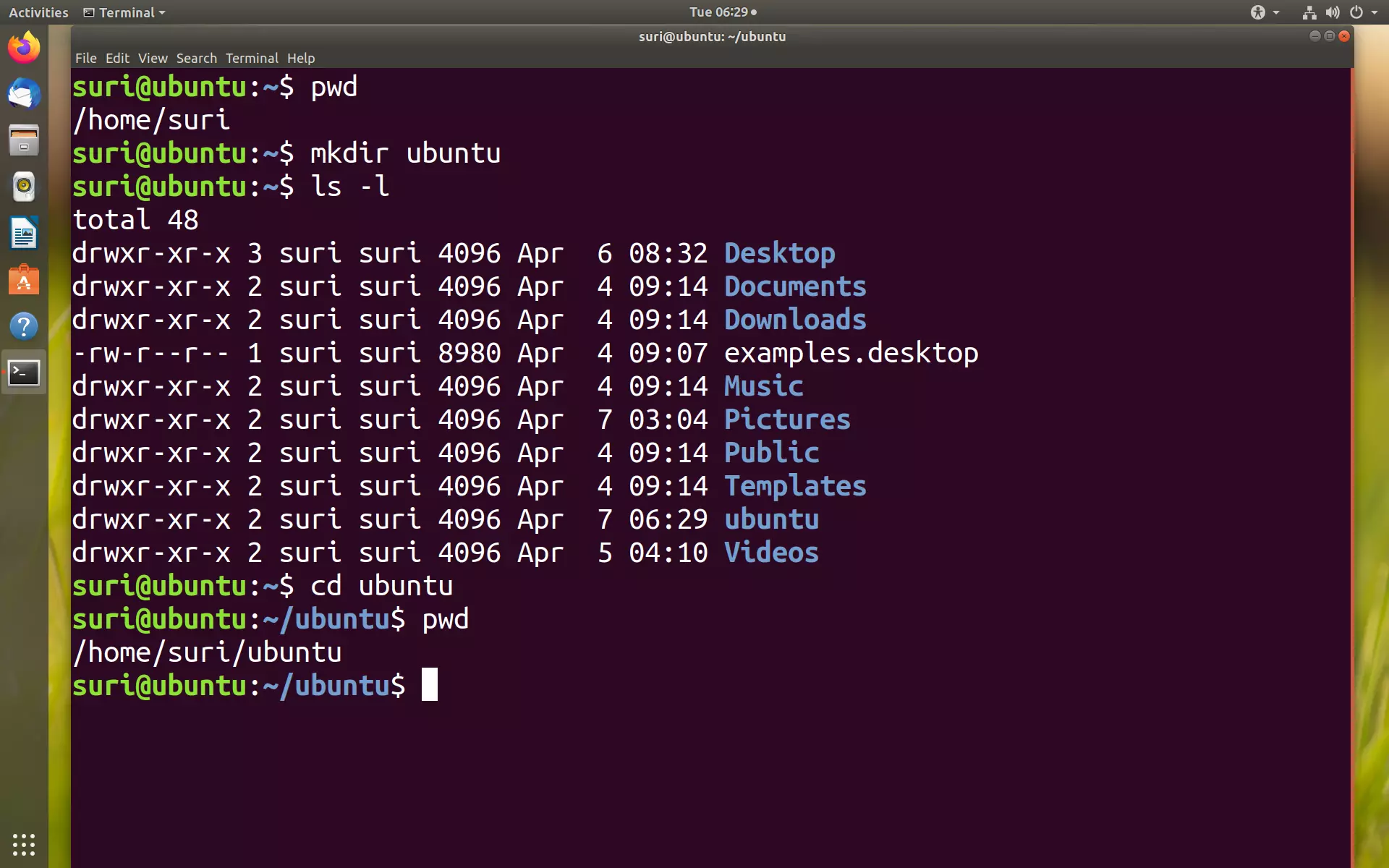
rw-rw-r– 1 maverick maverick 1176 Feb 16 00:19 1.cġst Character – File Type: First character specifies the type of the file. $ ls -l : To show long listing information about the file/directory. Display All Information About Files/Directories Using ls -l ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Examģ.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.We named files auth.log* because old auth.log files are gzipped and have gz extension.
We will filter for “auth” for all files named auth.log*. Grep is a very capable tool to filter log files. Searching is a way to see occurrences in a log file and previous and next events. After arriving at the file end if no match exists we will get a message like below at the end of the terminal. To continue to search term without entering, again and again, press n for the next match or p for the previous search. After opening log files with less use /auth to search “ auth” term down to the file pages. Less have the functionality to search a text file were in this situation a log file. Space will skip to the next page also page up / page down will work too. There are different methods to read log file but we will use less which have practical solutions while reading the log file. $ ls -R /var/log/ List Log Files Reading Log Files We can list in a recursive manner to get files and folder under /var/log directory like below. Logs files can be simply listed by using ls command but keep in mind there are directories they contain different files for logs.
LIST FILE DETAILS LINUX HOW TO
In this post, we will look at default log files and how to list, tail, search, filter these logs.

There may be some exceptions like third party applications but the configuration of log location can be changed to the /var/log directory. These files are generally located at /var/log . Linux provides a lot of different types of logs by default.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
